January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month and a reminder that the most important thing you can do to prevent cervical cancer is to start screening at the age of 21. The American Cancer Society estimated that about 13,800 new cases of invasive cervical cancer would be diagnosed and about 4,290 women would die in the US in 2020. While cervical cancer used to be the most common cause of death in women, survival rates have increased as Pap tests and human papilloma virus (HPV) testing have become more customary.
Types of Screening
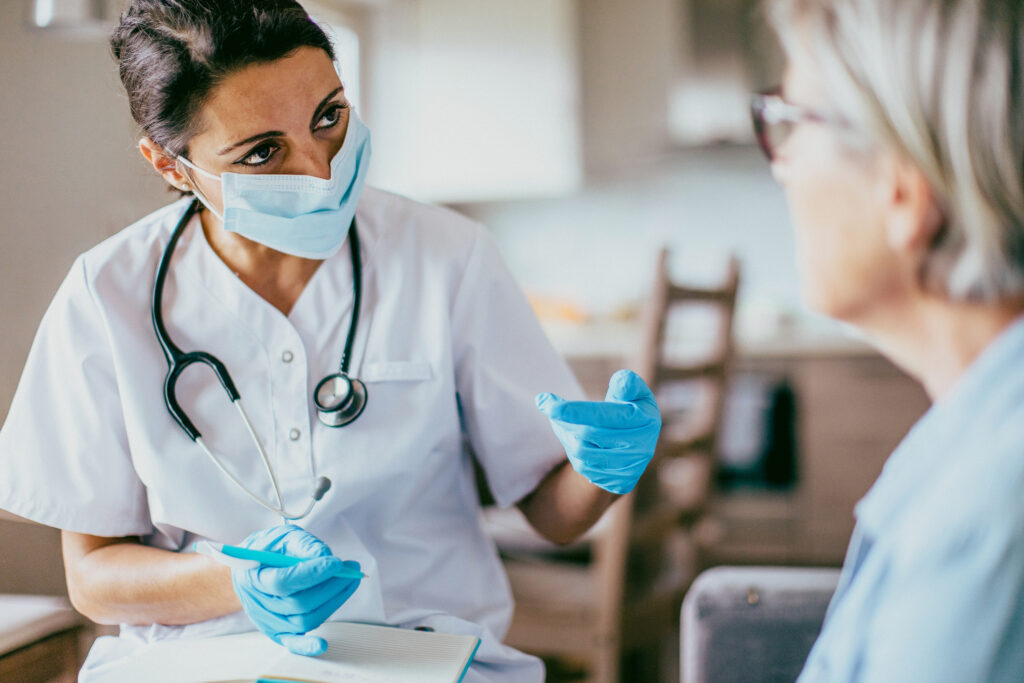
A Pap test is a procedure that collects cells from the cervix so that they can be analyzed in a laboratory for cancer and pre-cancer. The collection is typically done during a pelvic exam by your healthcare provider who gently scrapes or brushes cells from your cervix and sends them to a laboratory for testing.
According the CDC, human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection and causes 9 out of 10 cases of cervical cancer. The HPV test can be done alone (primary screening) or at the same time as a Pap (cotesting) using the same cell collection method.
How Often Should You Get Tested?
Test frequency recommendations have changed over the years; however, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) currently recommends that patients (with exceptions) follow these guidelines:
- If you are younger than 21 years—you do not need screening.
- If you are aged 21–29 years— have a Pap test every 3 years.
- If you are aged 30–65 years—you can choose one of three options:
- Have a Pap test and an HPV test (cotesting) every 5 years
- Have a Pap test alone every 3 years
- Have a primary screening (HPV) test alone every 5 years
- If you are 65 years or older—You do not need screening if you have no history of cervical changes and either three negative Pap test results in a row or two negative cotest results in a row within the past 10 years, with the most recent test performed within the past 5 years.
Screening Options with GenPath Women’s Health
Genpath Women’s Health, a division of BioReference Laboratories Inc., offers a number of different tests appropriate for the diagnosis of cervical cancer as recommended by ACOG. Testing options include a Pap Test only, a Pap Test and an HPV Test (cotesting), Pap Dependent HPV (a unique cotesting approach to cervical cancer screening, developed by GenPath, which maximizes the opportunity to detect your risk of cervical disease by matching the appropriate HPV test to your Pap results), and Primary Screening (HPV Testing only).
Speak with your healthcare provider to determine which test is medically appropriate for you.
If you are a healthcare provider, click here to become a customer and learn more about our screening options for cervical cancer.
Sources:
American Cancer Society
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cervical-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cervical-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/screening-tests/hpv-test.html
CDC
https://www.cdc.gov/std/hpv/stdfact-hpv.htm
https://www.cdc.gov/hpv/parents/cancer.html#:~:text=More%20than%209%20of%20every,that%20can%20lead%20to%20cancer