Diabetes Testing
Understanding your glycemic variability will help your healthcare provider provide personalized care for your diabetes. Speak with your healthcare provider to confirm if GlycoMark testing is right for you.
Este sitio web (y las páginas contenidas) estan desactivado. Si se necesita asistencia en español u otro idioma, por favor llame sin cargas a 800 229 5227.
| Code | SST | 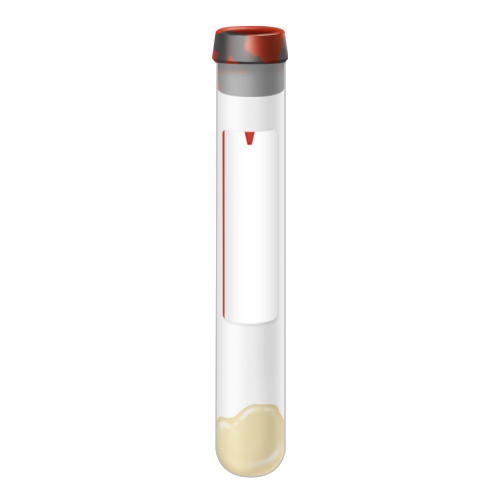 |
|---|---|---|
| Name | SST Tube | |
| Code | BML | 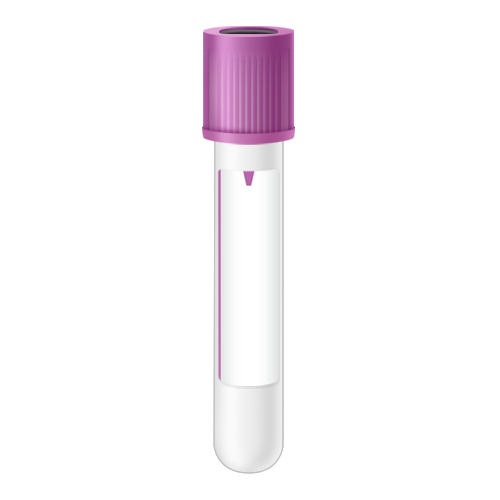 |
| Name | Bone Marrow - Lavender Top | |
| Code | LAV |  |
| Name | Lavender top- EDTA | |
| Code | FLUL |  |
| Name | Fluid Lavender (source required) | |
| Code | TAN |  |
| Name | Tan Top | |
| Code | YEL |  |
| Name | Yellow top- ACD | |
| Code | YELS |  |
| Name | Yellow top- SPS | |
| Code | RBP | 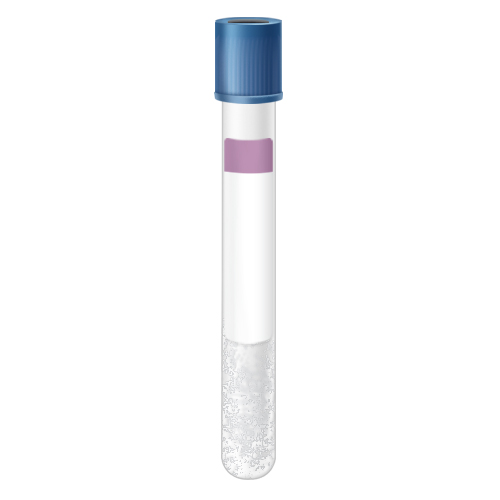 |
| Name | Blue-Royal Blue Top K2 EDTA Plasma(*LAVENDER LINE) | |
| Code | RBS | 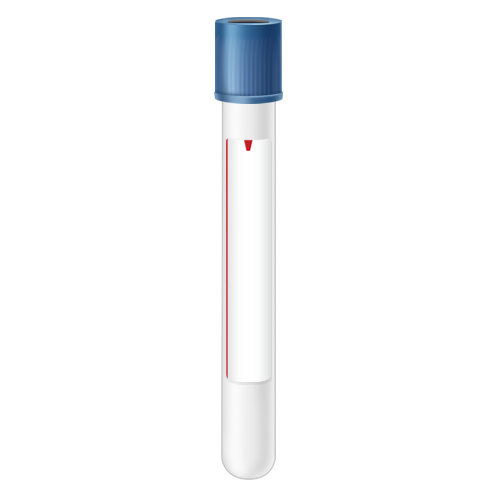 |
| Name | Blue-Royal Blue Trace Element Serum (**RED LINE**) | |
| Code | URB |  |
| Name | Blue-Royal Urine | |
| Code | GRY |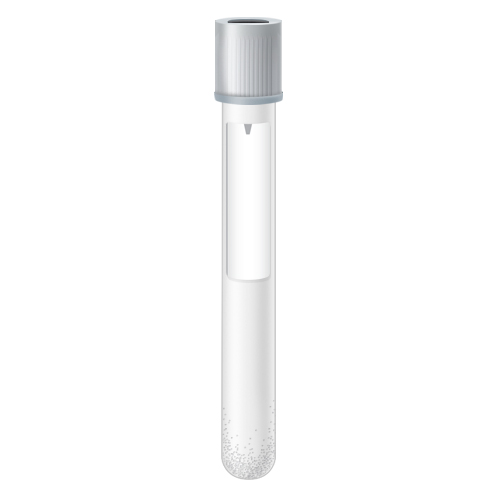  |
| Name | Grey top- Sodium Fluoride | |
| Code | BMG |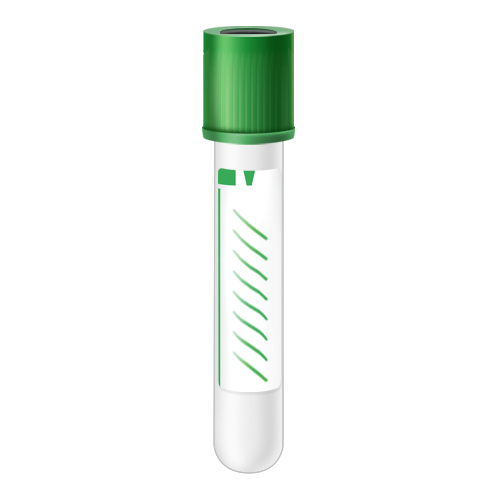  |
| Name | Bone Marrow - Green Top | |
| Code | UG |  |
| Name | Green top urine | |
| Code | UGTP |  |
| Name | Green top urine (preservative) | |
| Code | FLUG |  |
| Name | Fluid Green Top | |
| Code | QFT |  |
| Name | Green Top-Lithium Heparin | |
| Code | FLUR |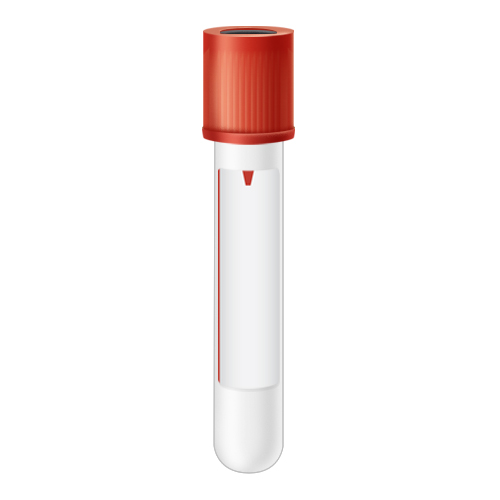  |
| Name | Fluid Red Top | |
| Code | LTB |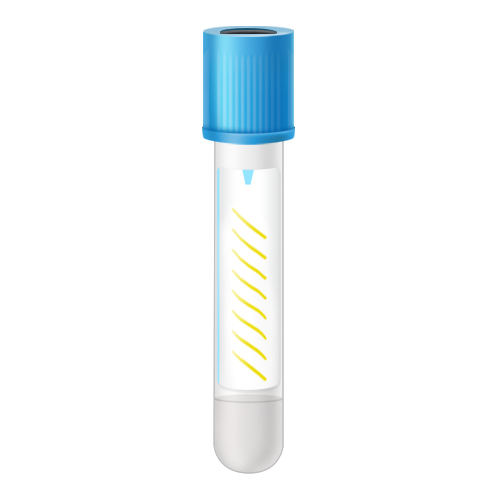  |
| Name | Light blue top | |
| Code | PPT |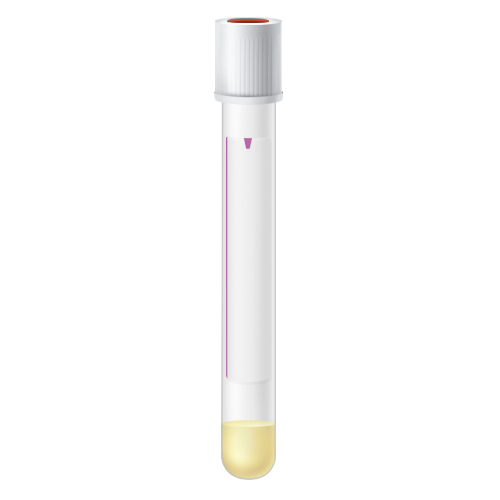  |
| Name | White Top (PPT) | |
| Code | ACDNA |  |
| Name | Ariosa Cell-Free DNA (White TopTube) | |
| Code | TP |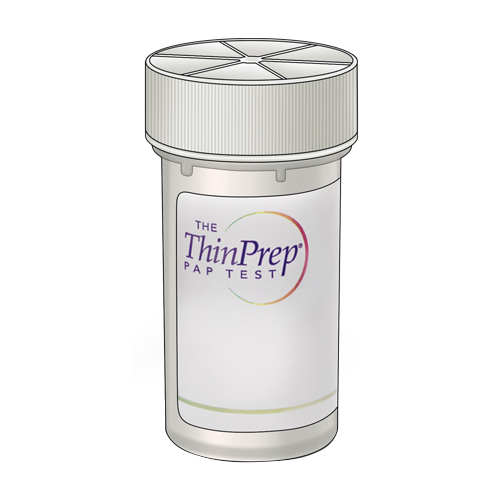  |
| Name | ThinPrep Vial | |
| Code | SPTH | 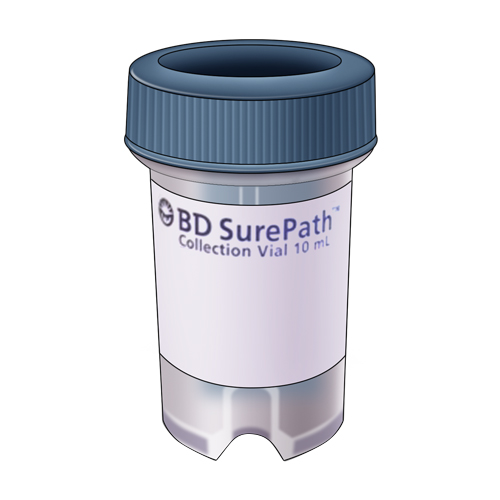 |
| Name | Surepath Vial | |
| Code | O&P | 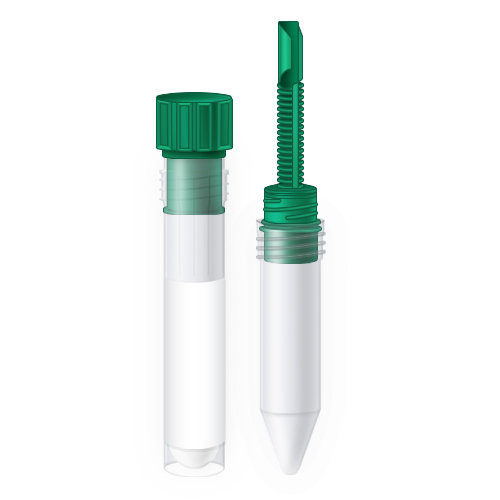 |
| Name | O&P Kit (Total Fix) | |
| Code | U24 |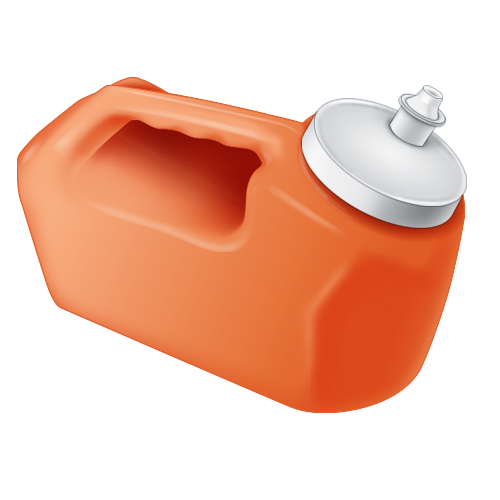  |
| Name | Urine Container - 24hr | |
| Code | UA |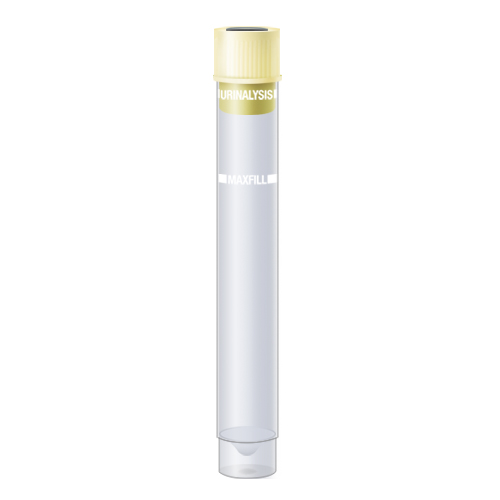  |
| Name | Urine Urinalysis Tube - Yellow | |
| Code | CUL |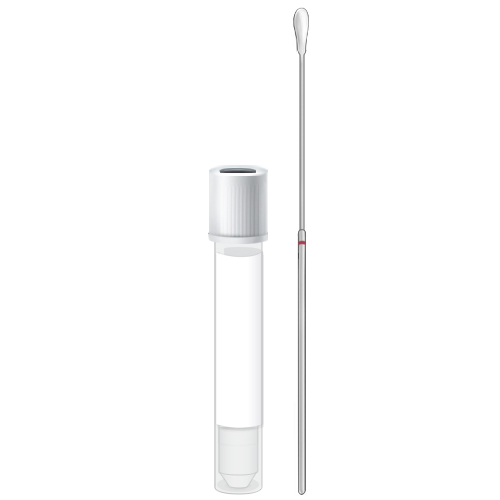  |
| Name | Swab-Bacterial Culture | |
| Code | ES |  |
| Name | Swab-E | |
| Code | APT |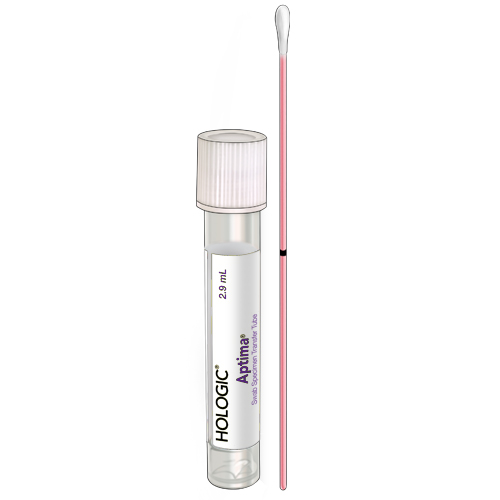  |
| Name | Swab-Aptima Genprobe | |
| Code | UGP | 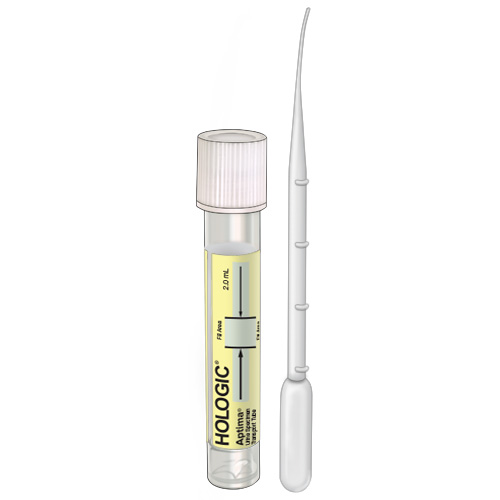 |
| Name | Urine Container-Genprobe-Aptima | |
| Code | BDA |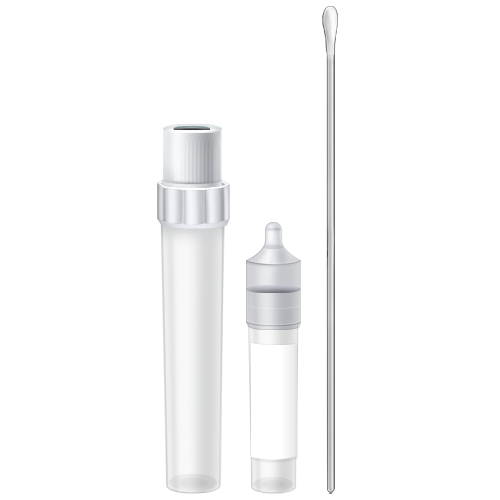  |
| Name | Affirm(BD) VPIII | |
| Code | RED |  |
| Name | Red Top Plain | |
| Code | UGY |  |
| Name | Urine Tube - Grey Top | |